When a comment landed here today from Diane O’Donovan about the (sometimes asserted, sometimes denied) connection between the Voynich Manuscript’s Q13 (the ‘balneo’ folios) and the late 12th century De Balneis Putolanis by Peter of Eboli, it reminded me that there’s a 15th century balneological manuscript out there I really want to know a lot more about – MS Aldini 488 “Collectio de balneis”.
Q13A vs Q13B (again)
However, before I launch into all that, I first need to recap various codicological features of Q13 before we start trying to work with it.
The first thing to know about Q13 is that its bifolios have ended up bound in the wrong order. We can tell this because a bifolio that was originally at the centre of a quire / gathering has ended up not at the middle. Moreover, following the logical through to the end leads (as per The Curse of the Voynich back in 2006) to a situation where you can reconstruct the central two bifolios’ nesting order: f84 – f78 (centre) f81 – f75.
The second thing to notice is that the drawings on these two nested Q13 bifolios (which are all about bathing ‘nymphs’) seem to sit in a quite different category from the drawings on the other three Q13 bifolios (which largely revolve around plumbing, though whether this is real or imagined is hard to say). Voynich researcher Glen Claston proposed that the first two bifolios form a balneological quire on their own (which he called “Q13B”), while the other three form a medical quire (which he called “Q13A”). Regardless of whether you agree or disagree with his specific interpretation, his basic codicological division into two separate artifacts has stood the test of time: so it seems we are looking at two separate (though similar-looking) things whose constituent bifolios have ended up interleaved. Glen also proposed that Q13B was constructed before Q13A.
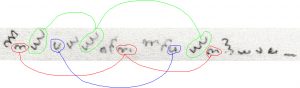
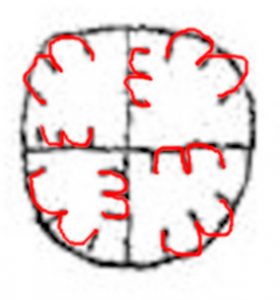
The third thing to be aware of is that on the Voynich Manuscript’s page f81r (in Q13B, the bathing nymphs section), there is apparently a poem. I raised this poem section as something which we might look for parallels with in other texts when I started discussing the ‘block paradigm’ approach (where you look for structural matches between a page of enciphered text and plaintext pages from similar contemporary or earlier manuscripts). Interestingly, it seems (from the line-initial gallows characters) that the f81r poem has a 7 / 8 / 8 / 8 line structure, which would be consistent with the writer / copyist having accidentally skipped past a line within the first block of the poem.
Putting all these pieces together, the implication is that we should be looking for a block-sized match between the contents of the two “bathing nymphs” bifolios and 14th / early 15th century balneological texts (which are possibly but not necessarily illustrated). The poem embedded in the middle (it’s on the right half of the central bifolio) seems to be structured as three verses, each containing four couplets (i.e. eight lines). This is because if we can find a source match that’s tolerably close to this basic ‘block specification’, we might just be in business.
Arnold C. Klebs
Back when I was writing The Curse of the Voynich in 2006, to be honest I hadn’t yet found much balneological source material at all. It was only a little later (in 2009) that I found an online version of the (1916) article “Balneology in the Middle Ages” by Arnold C. Klebs. This mentioned a number of late medieval / early modern people who had written on the subject of baths, e.g.:
- Giovanni de Dondis
- Gentile da Foligno (d. 1348)
- Ugolino Caccino of Montecatini (d. 1425)
- Matteo Bendinelli (1489)
- Michele Savonarola (who I already knew about)
Klebs also mentioned the printed book “De Balneis omnia quae extant” Venice, Giunta, 1553, fol., 447 leaves, which he describes as “the first text-book on balneology“.
A source Klebs also refers to specifically for German bath history is:
- Martin, Alfred “Deutsches Badewvesen in vergangenen Tagen,” Jena, Diederichs, 1906. With 159 illustrations from old originals.
Giunta’s (1553) De Balneis Omnia
Google Books lists two separate copies of Giunta’s (1553) “De Balneis Omnia Quae Extant apud Graecos, Latinos et Arabas” (etc etc), both of which freely downloadable:
The bad news is that this is a super-heavyweight Latin compendium of balneological sources (the PDF runs to 1033 pages). However, the good news is that Giunta has assembled it from just about everyone pre-1553 who had written about baths, water etc: so there are large sections excerpting books from early authors such as Pliny, Avicenna, Aristotle, Galen, Hippocrates, along with selections from 16th century authors such as Gesner, Fuchs etc.
One thing I found was that, Pietro d’Abano’s “De Balneis” aside (which is written in hexameters), almost none of the balneo sources quoted by Giunta seem to appear in verse form. Even the promising-looking verse section on p.90 by “Ioannis et Iacobi De Dondis Patavinorum” turned out to be a poem by Claudian (370AD-404AD) (“Fons, Antenoreae vitam qui porrigis urbi, / Fataque vicinis noxia pellis aquis“).
Having said that, Giunta’s selection is entirely in Latin and far from complete. So it may well be that, if we can somehow go back to some fifteenth century collection of balneo manuscripts, we can see these in their original form – which may well be in Tuscan (rather than Latin), in verse (rather than in prose), and illustrated (rather than just text).
But where on earth would we find such an unlikely-sounding text?
Pavia, MS Aldini 488
It turns out that there really is such a text: and it is at the University of Pavia. Sadly, this “Collectio de Balneis” hasn’t yet been digitized (or if it has, its digital pages have not yet been shared outside the University of Pavia). But we do know the contents of MS Aldini 488:
Aldini 488, Collectio de Balneis. Cart., sec. XV, cc. 78 n.n., 232 x 154 mm.
c. 1: Savonarola Michele, De balneo et termis naturalibus omnibus Italiae sicque totius orbis proprietatibusque earum
c. 45: Ugolino da Montecatini, De balneis mineralibus et artificialibus
c. 61: Epigrammata de balneis puteolanis
c. 66: Consilium pro balneis de Corsena in comitatu luchano pro domino Lanzaloto de Crotis ducali consiliario
c. 67: Tura di Castello, Regula et tractatus balnei de poreta
c. 68v: Tractatus pro balneis de aquis per Petrum de Tussignano
c. 70v: Antonii Guaynerii papiensis de balneis aquis ciuitatis antiquissime que in marchionatu montisferrati sita sunt tractatus
c. 74v: De balneis secundum Petrum de Ebano
c. 75v: Tractatus de balneis secundum Gentillem
c. 76v: De balneis de Burmio secundum magistrum Petrum de Tussignano
c. 77v: Regula balnei loci de Aquaria in territorio regii
c. 78v: De balneo aque porrete
Collocazione cd: Mediateca nas bu 269
Collocazione vol. originale: Aldini 488
Because this is not yet available online, it is where – unless you happen to know better? – our current breakneck tour of balneological sources stops,
Note that there are a fair few monographs on individual balneo authors:
- This Spanish Prezi presentation by Sergio P on Michele Savonarola lists eight manuscript versions of his book on baths (including Paris BNF Nouv. Acq. Lat 889, dating to 1452), seven printed versions of the same (1485-1562), plus four separate monographs.
- Pietro da Tossignano’s (d. 1401) “Tractatus de regimine sanitatis” was printed in 1535 (his medical recipes are online here). Giuseppe Mazzini wrote “Vita e opera di maestro Pietro da Tossignano” in 1926 (reprinted in 2007).
As an aside, I also found an interesting chapter (in French) on the balneo literature – “Les traités médicaux sur les bains d’Acqui Terme, entre XIVe et XVIe siècles“, by Gabriella Zuccolin – from a recent book, “Sejourner au bain”. Zuccolin further notes that many of the treatises are covered at speed by Lynn Thorndike, but… they would be, wouldn’t they?