We start with some film footage of the Atlantis, taken by a doctor called Karl Höffkes who worked aboard the raider. I’m not sure, but the brief glimpse of vehicles that appears at 0:13 might well have been taken aboard the Tirranna:
According to Captain Gundersen (interviewed for the maritime hearings in Oslo in December 1940), “it turned out that” five people died in the 10th June 1940 attack by the Atlantis, as transcribed here.
– 4th engineer Einar Christensen,
– Electrician Otto Kristensen,
– Matros [?] Hilmar Engelsen,
– Machine Boy James Andersen,
– Passenger Charles Mikkelsen
On its own, this would be strong evidence that Mikkelsen died. However, we can further cross-reference this with a number of other accounts, and confirm that exactly five people died on the 10th June 1940…
Graeme Cubbin
John Richardson’s excellent ebook “Victims of Atlantis” includes many details taken from the diary of 16-year-old cadet Graeme Cubbin (who was on the SS Scientist, a ship captured by the Atlantis a few weeks before the Tirranna), including the following quotations:
When Captain Gundersen met up with Rogge he complained bitterly, saying that Norway had capitulated and made peace with Germany just a few hours earlier on that very day, and that he had quite unnecessarily killed five of his men and badly injured a dozen more. (p.51)
Also:
Quite a number of [the Norwegian crew of the Tirranna] were working their passage home from Australia. They did so in order to join up and help put a spoke in the wheel of the Nazi War machine; several had lost their families in the German bombing raids. Five of their comrades had been killed by the German gunners, another died later in the hospital of Atlantis and several lay wounded and helpless in the care of the German doctors. (pp.53-54)
Ulrich Mohr
According to Atlantis’ First Officer Ulrich Mohr (in his book “Ship 16: The Story of a German Surface Raider”):
When I climbed aboard [the Tirranna] I found her decks were literally covered in blood; it lay in pools wherever one trod. Five men were dead, but there were many wounded.
Kapitan Rogge – Atlantis Ship’s Log
Personally, I found reading Volume 1 of Captain Rogge’s Ship’s Log for the Atlantis (thankfully in English) to be shocking and humbling: it taught me more about the real nature of sea warfare than any other book I’ve read. The Kapitan’s behaviour was a model of precision, insight, care and yet cunning: he even used the Tirranna as a sighting target at night to see which one of the different sets of binoculars on board was most effective at picking out ships in the dark.
From Rogge’s log, it is amply clear that he was fully aware of the five deaths on 10th June 1940. Note that the next death wasn’t on the 11th (as reported by Captain Gundersen) – in fact, the Tirranna’s carpenter Johan Johansen had a leg amputated plus an emergency appendectomy (!) on the 11th, but died on the 15th. All in all, the Atlantis’s log seems to be an extremely reliable source document to be working with.
The account of the taking of the Tirranna starts on about page 93 and continues for many pages. After capturing the Tirranna, the Atlantis was in close contact with its prize ship for a good amount of time, so there are numerous mentions of the Tirranna throughout the log.
(p.97)
12:44 — Picket boat sent off with search party under the command of Lt.Cdr. Kamenz. They established the following:-
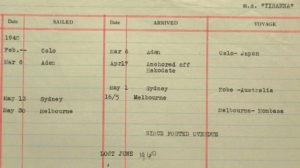
Motor ship “Tirranna” (built in 1938 by Schichau in Danzig) 7230 tons, carrying 3,000 tons of wheat, 72,000 sacks of flour for British Ministry of Food, 6,015 bales of wool for the British Government, 178 military vehicles and a cargo of canteen goods for the A.I.F. (Australian troops in Palestine) sailing
(p.98)
under orders from the Admiralty from Melbourne to Mombasa. The crew had not yet left the ship, as the boats were partly destroyed. The upper
deck of the ship showed signs of the long spell under fire. There was hardly a spot on the whole ship which had not been riddled with splinters. The upper bridge had been especially hard hit, likewise the boat deck, where the sandbagged radio cabin and the mess below it had been destroyed by a direct hit. Numerous casualties, dead and wounded, lay about the ship. She requested a doctor to look after the wounded and Surgeon Lt. (j.g.) Sprung went aboard shortly afterwards. He certified the death of 5 men and saw to the transport of 3 severe casualties. The crew were made to pack up their private gear and then took to the boats under the supervision of Lt. (j .£•) Breuers • To ease the boat traffic, the motor boat from the “Europa” was sent out and proved invaluable. I must say, however, that the crew has had to toil for weeks to get this boat, which came from one of Germany’s first passenger ships, fit for use at sea and in a decent condition. Boatswain’s mate Ross maneuvered very well with this rather unmanageable boat.Under weather conditions to date the naval pinnace has proved itself invaluable for all tasks. The boat has been handled very carefully and with extremely fine seamanship by the regular steersman Boatswain’s Mate Stierle.
Surgeon Lt. Cdr. Reil and Surg. Lt. (j.g.) Sprung, the sick bay attendants and the stretcher bearers gave most excellent and devoted care to the severely wounded casualties. As the surgeon, Lt. (j.g.) Sprung had to perform difficult operations – an amputation and a brain operation. Lt . (s.g.) Strecker assisted at the operations. In all six severely wounded casualties had to receive treatment.
[…]
(p.99)
11 June — A statement made by the captain gave us the Tuesday following information:- “Tirranna” left Oslo on 18 Feb, 1940, proceeded through the North Atlantic, Mediterranean, Suez Canal to Ras Hafun, took in salt there, proceeded on 19 March to Miri (Borneo) where she took in oil (29 March) to Hakodate (Japan) on 6 April. There the ship heard news of the outbreak of war between Germany and Norway. On 17 April 1940 while he was in Hakodate the captain received orders from the Norwegian consul in Tokyo to proceed in ballast to Sydney and take in cargo there for British customers, and await further instructions. The ship stayed in Sydney from 1 till 14 May, 1940, in Melbourne from 16 to 29 May. During her stay in Melbourne the ship was fitted out with a 4.7 inch gun, (quick firer 4.7 inch, 45 cal. K.1917 Kure P.V.) (built in Japan under an English license no. 338 Sept. 1932) base, magazine, smoke floats, gun communication telephone, 1 machine gun and 3 rifles, together with ammunition, steel helmets, etc. all to the account D.E.M.S. No. 91 (Defensively Equipped Merchant Ships ).
(p.100)
According to the captain the “Tirranna” is the first armed Norwegian merchant ship to sail for the Department of Defense, Commonwealth of Australia.He took on the main part of the cargo in Sydney, the remainder of the lorries in Melbourne. From there the ship was despatched on 30 May to Mombasa. The captain went on to state that he received his course instructions for Mombasa in Melbourne. He had destroyed them on meeting, the auxiliary cruiser i.e. he had torn them up and put the fragments in the waste paper basket. After the waste paper basket had been emptied carefully, we were able to piece the instructions perfectly together again (see appendix). Also the Naval Control Officer in Melbourne had
assured him he could go to sleep quite happily until he reached Mombasa, there were no German warships in the Indian Ocean, However, there were mines off Cape Agulhas, which had been laid by the “Graf Spee”.
[…]
(p.101)
The captain thought that he might be shot on board the auxiliary cruiser. He bitterly reproached himself for his conduct and its consequences – above all for the five dead.
So, All That Is Missing Is…
Naturally, there’s one last thing we don’t have, because the list of the names of the Tirranna’s crew and passengers is in an appendix in the original (German) Atlantis ship’s log, which (unfortunately for us) the American translators apparently thought not to include.
So… can anyone help find the original Kriegsmarine document (presumably Volume 2)? I couldn’t find any reference to it, but given that it was translated, it must be somewhere out there, surely?
Alternatively, the crew list and the list of the five dead might be included in Rogge’s own book (which went through at least ten editions in German, and was translated into English). The bibliographic reference given on the German Wikipedia page is:
Wolfgang Frank, Bernhard Rogge: “Schiff 16. Tatsachenbericht. Die Kaperfahrten des schweren Hilfskreuzers Atlantis auf den 7 Weltmeeren.” Genehmigte Taschenbuchausgabe. 10. Auflage. Heyne, München 1982, ISBN 3-453-00039-0, 251 S
Does anyone have a copy of this? Alternatively, the English translation was published as “Ship 16: The Story of a German Surface Raider” (which sadly doesn’t have as gloriously pedantic a title as the German original) [and yes, I’ve ordered myself a copy of this too, *sigh*].