Seeing an advert on the side of a bus for the film “Nuremberg” yesterday reminded me of an aspect of Nick Redfern’s “Body Snatchers in the Desert”. There, Redfern put forward an (occasionally) sketchy but (definitely) alien-free account of the Roswell Incident. In 2017, he described his book as “the Roswell-themed story that UFOlogy hates and which, back in 2005, made [him] public enemy number one“.
For Redfern, 1947 was a key moment in history, not so much because of the main Nuremberg trials (which had finished in late 1946), but because of the Doctors’ Trial, which ran from December 1946 to August 1947. Twenty physicians and three SS officials were charged for their involvement in:
- Aktion T4 – ‘involuntary euthanasia’ [i.e. mass murder] of disabled and mentally handicapped people
- Nazi human experimentation – 15,000 documented victims, though the real total was much higher
Seven were hanged, five got life imprisonment, four got prison sentences, and seven were acquitted.
Redfern, thanks to his informant “The Black Widow”, built up an account of Roswell where the ‘little aliens‘ in the aluminium capsule were in fact handicapped Japanese people (with progeria, etc). And so in mid-1947, the shadow of Nuremberg’s Doctors’ Trial hung heavily (he believed) over all the people involved in these human experiments that were all too similar to that which those Nazi doctors were very publicly on trial for.
Radiation Exposure and Cosmic Rays
The obvious question: what on earth was so important about balloon experiments circa 1947 that American biophysics researchers would even consider Nazi-style human experimentation as an option, let alone actually doing it? For the Black Widow, this was all about Oak Ridge’s “research into understanding high-altitude flight and exposure on the human body for the military [and] how that tied into plans NEPA would have to one day build nuclear aircraft that would be able to fly at [very] high altitudes […] for long periods.” (Body Snatchers, p.7)
One of the US military’s key strategic fears 1945-1950 was to do with cosmic rays: the concern (which we now know to be hugely exaggerated) was that people working in the stratosphere for extended periods might just suddently die from exposure to (what were thought to be) violently powerful cosmic rays. And so – the argument runs – there were medical committees in 1946-1947 who were trying to get an answer to this problem by any means possible. And if that involved what we would consider unethical means? They apparently didn’t care. Until the Nuremberg Doctors’ Trial forced them to care.
Redfern (and indeed the Black Widow) frames this in terms of Operation Paperclip, i.e. that it was all the fault of those nasty German and Japanese scientists swooshed into America in the post-WWII mayhem, bringing their unethical research values in with them. But to be fair, I’m currently looking at the lists of people on medical committees (e.g. the AEC’s ABRC), and I’m honestly not seeing any Paperclippers there. The uncomfortable truth? Back then, it wasn’t necessary to be a Nazi or a member of Unit 731 to have extraordinarily suspect ethical values, if you thought that would ‘get the job done‘.
David DeVorkin and Project Helios
With this whole highly politicised (I nearly typed “highly charged“) cosmic ray situation in mind, I’m now re-reading David DeVorkin’s “The Race to the Stratosphere”: this covers high-altitude scientific ballooning either side of WWII, and (archivally) is exceptionally strong on the bodies and committees that collectively defined what science would get funded (and so what Science would become) post-WWII.
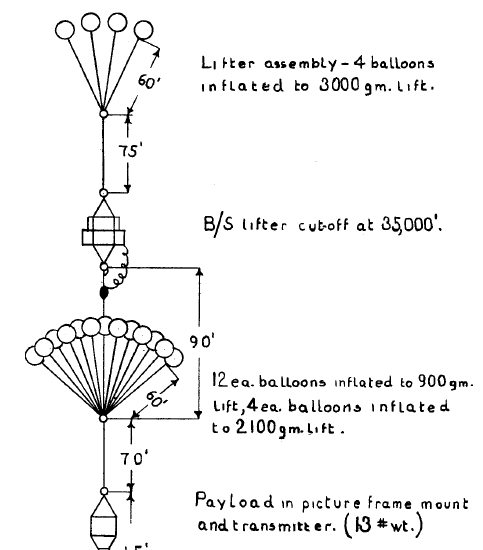
To my mind, these committees had perceived Project Helios as the knight in shining armour that would help get the stratospheric data they needed to resolve their issues and strategic fears. So it was extremely awkward for them all when that project stumbled, faltered, and got cancelled in the first few months of 1947. Jean Piccard had proved to be a terrible project principal, and his Great Big Plan to get people (to be honest, mainly him and his wife) to the stratosphere using his plastic balloon clusters had been exposed as just a little bit too hopeful for the ONR. So the US Navy kicked Piccard out, and subsequently split Project Helios into an unmanned half (Skyhook) and a manned half (Project Manhigh with Otto Winzen).
More generally, DeVorkin’s big idea is that manned scientific ballooning in the 1930s was a lot like manned rocket flight in the 1960s: and I think there’s a lot to like about this conceptual framework. But… to be honest, I’m now far from sure that the situation in the 1930s (for example, with cosmic rays) is an accurate guide to the situation in the later 1940s. Which is why I’m now going to re-read his book really carefully, and then move onto his “Science with a Vengeance” (which I only found out about a few days ago).
To move this whole research thread forward, The Only Way Is Ethics…