Edith Sherwood, everyone’s favourite Leonardo-wrote-the-Voynich-so-he-did theorist, has posted up an extensive (and fascinating) new article focusing mainly on the depictions of the sun, moon and stars in the Voynich Manuscript: the starting point of her journey is the striking similarity between suns and moons in the VMs’ “astronomical” Quire 9 and a sun/moon pair on a particular Afro-Portuguese ivory horn (#101) carved between 1495 and 1521. Essentially, the question she tries to tackle is: what on earth connects these two very disparate objects?
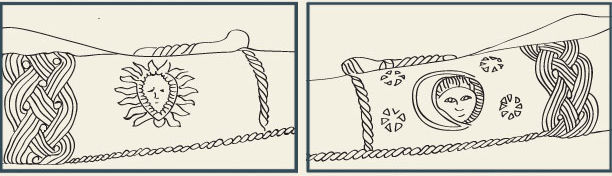 Afro-Portuguese Horn #101 (from Edith Sherwood’s site)
Afro-Portuguese Horn #101 (from Edith Sherwood’s site)
Unsurprisingly, she starts by linking the sun with the Visconti raza symbol (as per p.61 of my “The Curse of the Voynich”): but, even better, continues by connecting the sun/moon pair to two copies of Dante’s Commedia, as posted up by long-time Tarot researcher Robert V. O’Neill in Chapter 14 of his online article “Dante’s Commedia and the Tarot”. O’Neill suggests connections between the Commedia manuscript illustrations (Sherwood describes these as 14th century “woodcuts”, probably a typo) and the designs found on early Tarot cards, in particular his Figure 37 (“late 14th century”) and Figure 39 (“mid 14th century”), though unfortunately he doesn’t give MS references for them. To all of which I would also add the probable connection between the circular arrays of VMs zodiac nymphs and Dante’s description of concentric rows of angels in Heaven (as per pp.36-37 of “The Curse”).
At first glance, Sherwood’s proposed iconographic connection between the Visconti-Sforza Tarot sun/moon, the carved ivory sun/moon, and the VMs sun/moon (essentially, though the carved ivory and the VMs were unlikely to be directly connected, they both had the Visconti-Sforza Tarot as a shared ancestor) seems perfectly reasonable. In fact, it almost amounts to an excellent example of the kind of “Voynich Research 2.0” 14th-century-centred art history I blogged about recently.
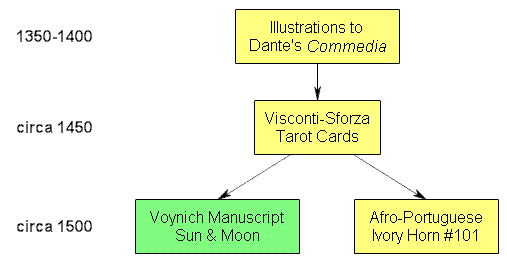
The problem with this is that it presupposes a circa 1500 (basically, Leonardo-friendly) date for the VMs, without noting that there is an alternative (and, given the 15th century quire numbers, I would say more likely) diffusion sequence that doesn’t rely on the Tarot at all. Remember, the similarities noted were between the VMs and the Commedia illustrations, not the Visconti-Sforza Tarot per se:-
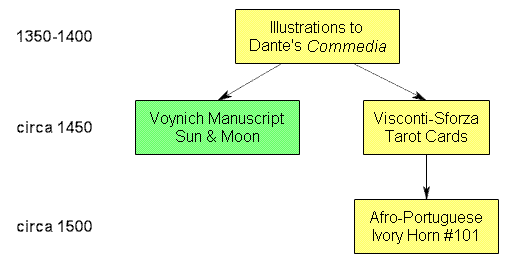
In her article, Edith Sherwood also makes a number of other fascinating observations and comparisons (to do with Apollo, with the water nymphs, and with the parallel hatching) which I’d really like to blog about in more detail, but quite frankly those will have to wait for another day.
Finally, Leonardo was anything but a child when he reached Milan in 1481 (when Sherwood suggests he probably first saw the Tarot), so her parallel claim that Leonardo can only have made the VMs as a (brilliant) child doesn’t really seem to stack up with her proposed Tarot connection anyway.
If you look at the VMs with truly open art historical eyes (as Sherwood set out to do), I think you will almost inevitably reach a certain position: it’s mid-Quattrocento Northern Italian, with its cryptographic roots in Milan, its intellectual roots in Florence, its stylistic roots in Venice, and its philosophical roots in Dante. Oh, and it was written by a secrets-obsessed right-hander with a far greater command of cryptography than Leonardo da Vinci ever had (Chapter 6 of “The Curse” has a detailed critique of Leonardo’s limited cryptography).
PS: I found Sherwood’s article through Google Adwords “Voynich written by a lefty?“: but if you want me to look at your Voynich site, please just email a link to me, it’s much cheaper (and quicker). 🙂